Indole test
General
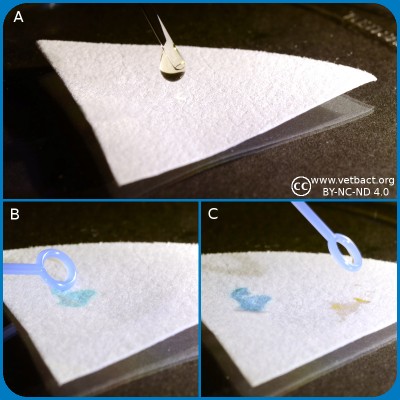
Spot indole test.
A. Application of spot indole reagent.
B. Application of indole positive bacterium.
C. Application of indole negative bacterium.
Click on the image to enlarge it.
Bacteria, which express the enzyme tryptophanase can hydrolyze the amino acid tryptophan to indole, pyruvic acid and ammonia. Presence of indole can be shown by means of Kovác's reagent or by spot indole test. In the spot test indole reacts with p-Dimethylaminocinnamaldehyde to produce a blue to blue-green product. Kovác's reagent contains p-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde, which forms a red complex with indole.
Method, spot indole test
- Place several drops of Spot Indole Reagent on a piece of filter paper.
- Fill a plastic loop with bacteria from a colony cultivated for 24-48 h.
- Rub it onto the reagent saturated area of the filter paper.
- Positive reaction: Appearance of a blue to blue-green color change within 10 seconds.
- Negative reaction: Remain colorless or light pink.
Method, Kovac´s reagent
- Suspend one colony from a pure culture of the bacterium to be investigated, in a suitable medium (for instance LTLSB or tryptophan medium).
- Incubate the medium at 37°C during 20-28 h.
- Add a few drops of Kovác's reagent.
- Positive test result: The indole reagent change colour to cerise red.
- Negative test result: The indole reagent remains pale yellow.
Use
Confirmation of suspected E. coli-strains. Typing (species determination) of Brachyspira spp. in combination with other tests. Kovac's indole reagent is more sensitive than the indole spot reagent, but it is not recommended for use with anaerobic bacteria. The indole spot reagen is suitable for both aerobic and anaerobe use.