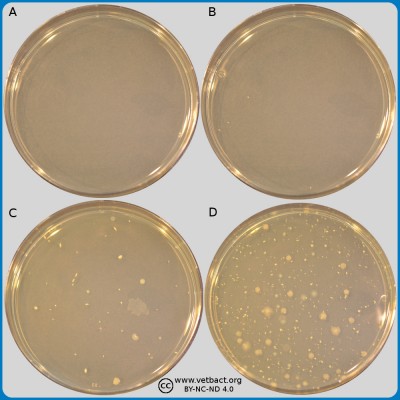
Plate count agar (PCA)The figure shows four PCA plates. Bacteria have not been cultivated on the plate in image A. On the plate in image B, 4 colonies could be calculated, on plate C 45 colonies and plate D >250 colonies. The plates in the images B, C and D originated from the same sample and have been been diluted by a tenfold dilution serie and the pour-plated by PCA. The plates have been incubated during 72 h at 30°C. - Click on the image to enlarge it. Image: Ingrid Hansson, Lise-Lotte Fernström och Karl-Erik Johansson (BVF,SLU)
ApplicationsPlate count agar (PCA) or Standard PCA is a bacteriological substrate used for determination of the total number of live, aerobic bacteria in a sample. Thus, PCA is not a selective medium. The amount of bacteria is expressed as colony forming units per gram (CFU/g), in solid samples and per ml (CFU/ml) in liquid samples. This value can be determined by making a tenfold dilution series of the sample. Then, 1 ml is taken from each dilution and applied on a petri dish and an overlay of 10-15 ml PCA is added by using the pour-plate technique, the plates are incubated at 20 or 30°C in three days. After incubation the number of colonies is counted on the plate with 25-250 colonies, which is considered to give the most accurate result. When calculating the actual number of bacteria in the sample, the dilution factor has to be considered. The medium contains:
The final pH of the medium should be 7.0 Other comments:The medium is straw-coloured (pale tan) and if colonies are present, they therefore also appear as straw-coloured. Updated: 2018-05-09. |