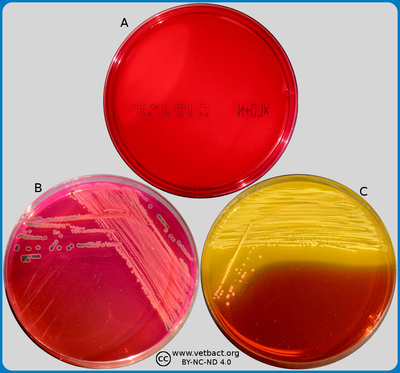
Xylose lysine deoxycholate agar (XLD agar)The figure shows three XLD agar plates. Bacteria were not cultivated on the plate in image A. On the plate in image B, Salmonella sp. has been cultivated. Note that the colonies are pink with a black centre. On plate C, E. coli has been cultivated. Note the colour change of the upper part of the plate, where E. coli (lactose fermenter) colonies appear.- Click on the image to enlarge it. Image: Karl-Erik Johansson (BVF, SLU) and Lise-Lotte Fernström (BVF, SLU).
Applications:Xylose lysine deoxycholate agar (XLD agar) is a selective growth medium, which is used for isolation of Salmonella spp. and Shigella spp. from clinical samples and from food. The pH of XLD agar is 7.4 and it contains the pH indicator methyl red, which gives a red or pink colour. Content of the medium:
Many enteric bacteria (except Shigella spp.) ferment xylose under acid production. Therefore, these bacteria form yellow colonies on XLD agar, but Salmonella spp. can decarboxylate lysin, which increases the pH and the colonies remain red. Furthermore, Salmonella spp. produce hydrogen sulfide (H2S) from thiosulfate, which results in a black precipitate with ferric salts. Other comments:
Updated: 2019-09-25. |